Copyright Independent Balkan News Agency, 2021
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Biogas-Plant.jpeg
1048
2000
Karrie Williams
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Pioneer-Logo-Color-min.png
Karrie Williams2021-11-17 21:25:392021-11-17 21:25:44Waste Burner Systems
Copyright Independent Balkan News Agency, 2021
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Biogas-Plant.jpeg
1048
2000
Karrie Williams
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Pioneer-Logo-Color-min.png
Karrie Williams2021-11-17 21:25:392021-11-17 21:25:44Waste Burner Systems
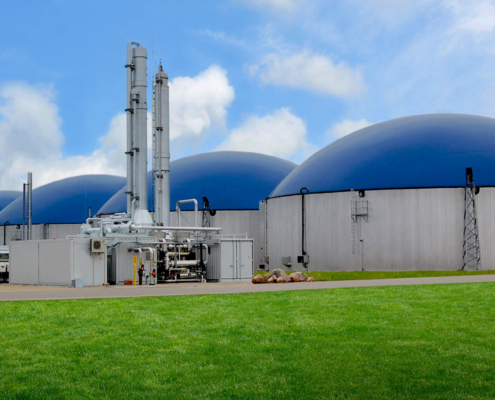
Over the last few decades, the production of biogas has increased rapidly. Biogas, a biofuel, has become a viable energy source due to its high content of methane and renewable characteristics. Today we will explore this environmentally friendly energy source in more detail.
How is Biogas Produced?
Biogas production is the creation of clean, natural gas (methane) that is of pipeline and common use purity. Specifically, biogas is about 50-70% methane and 30-40% carbon dioxide. Depending on the desired application, different purities of methane gas can be produced. This is done by refining the biogas after its initial production.
We will look at two primary means of biogas production in this article:
- Natural production through degradation of wastes, and
- Manufacturing biogas with anaerobic digesters.
Natural Production of Biogas
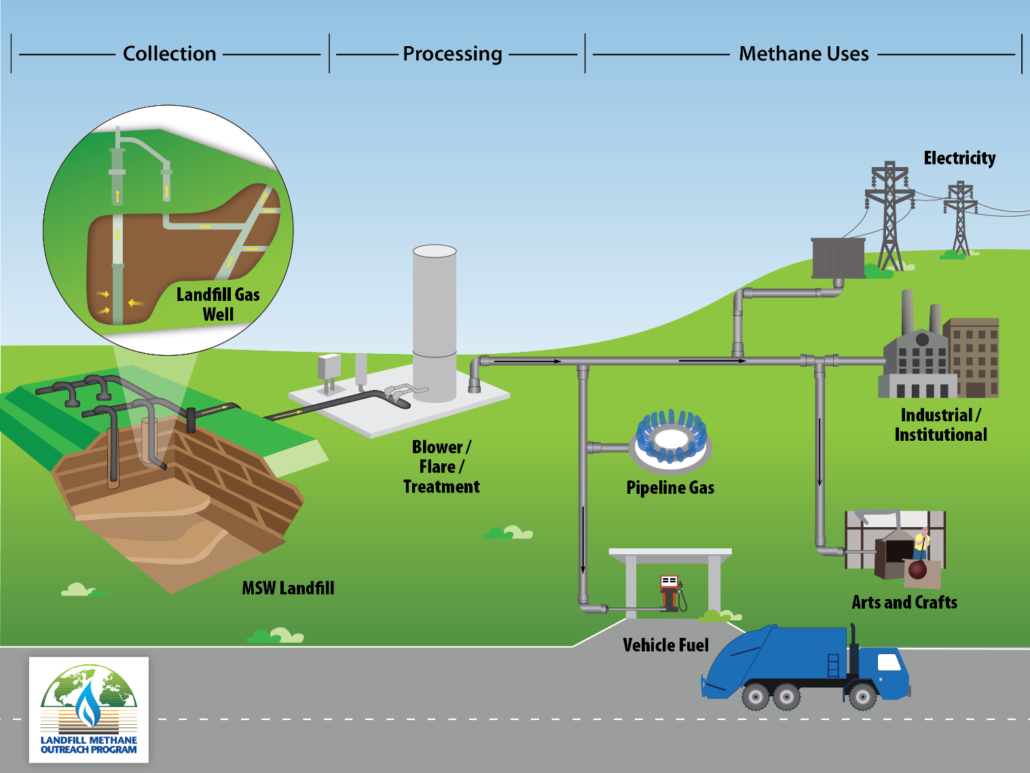
A good example of natural biogas production is landfills. Sanitary landfill operations emit methane, which can be captured and stored. Oftentimes, these operations have many cubic miles of natural waste degrading underground. Proper landfill infrastructure captures these emissions. So, less methane is released into the atmosphere, and more biogas is available for recycled use.
The captured biogas can be used to generate power on-site or sold to the local power grid for base load energy demand. It can also be refined further for use in compressed natural gas vehicles.
The Landfill Methane Outreach Program (LMOP) is a program set up by the EPA. They aid in the development of energy projects that reduce landfill emissions and produce biogas. You can learn more about this project and landfill gas by clicking here.
Manufactured Biogas
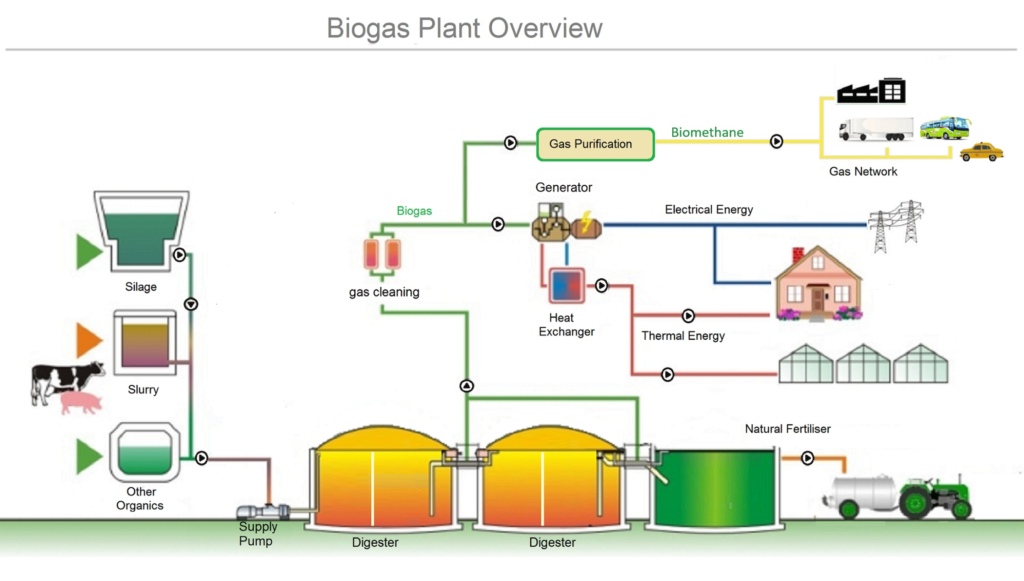
Some facilities are designed for the industrial production of biogas. They use equipment called anaerobic digesters to accomplish this goal. These facilities are a refinery of sorts, specializing in methane gas production from natural waste sources. The sources vary between farming waste, sewage waste, and food/beverage waste products. There is a lot of potential in these plants: think of all the spent grain in American breweries every day!
These wastes are put into anaerobic digesters, where microorganisms feast on them. The microorganisms naturally produce methane as a by-product. Then, the methane is extracted and separated from other by-products. And from waste, we now have fuel.
Anaerobic digestion technology is not a walk in the park, however. It requires expertise in product knowledge, operation, and servicing. At Pioneer Industrial, we help outfit facilities like these and keep them running efficiently.
How is Biogas Used?
Biogas for Electricity
One of the main uses of biogas is electric energy production, which we all use every day. Take a moment to think of electricity’s importance. We use it in lighting our buildings, or heating and cooling our homes. It functions major appliances, communication devices, and manufacturing equipment. Now it’s beginning to power more and more of our vehicles on the road!
Electricity production is vital to the world and societies we’ve developed. It is worth noting biogas’ potential role in this industry. The U.S. Department of Energy shares some interesting facts and numbers on its biofuel page. They estimate that biogas energy production could potentially satisfy 12% of the U.S. national electricity demand. And that’s from wastewater treatment alone! Keep in mind, wastewater treatment is not the only source of biogas. It is evident that biogas has the potential to meet a large percentage of our energy demands.
Biogas for Transportation Fuel
The previous section talked about biogas’ potential in fueling a new wave of electric cars. In the meantime, we still have a large demand for other transportation fuel sources.
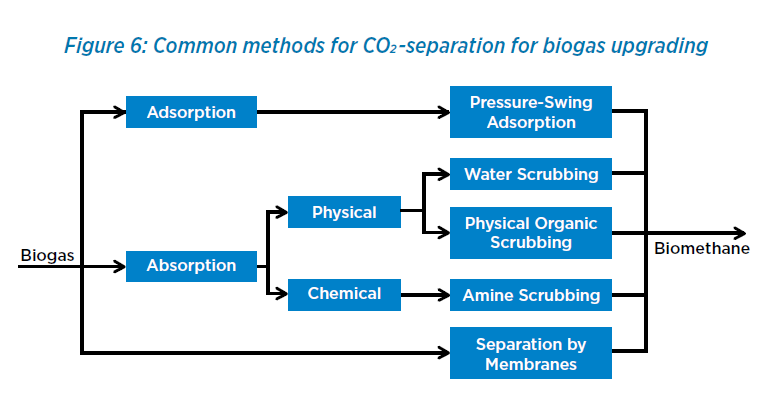
Biogas used for electrical generation is not as refined as it can be. This biogas is also known as raw biogas, being around 50-70% methane. To be suitable in engines that power vehicles with natural gas, it must be further refined. Biomethane is the upgraded version of raw biogas and is 90-99% methane.
By separating the CO2 from raw biogas, biomethane is created. This process is implemented in many operations that already work with biogas. For example, some landfills produce biogas and biomethane to power their facilities and vehicles. True sustainable energy at work!
Biogas Production Across the Globe
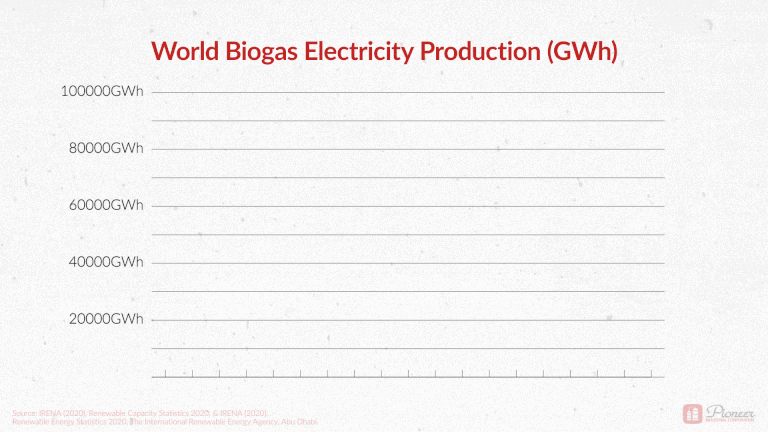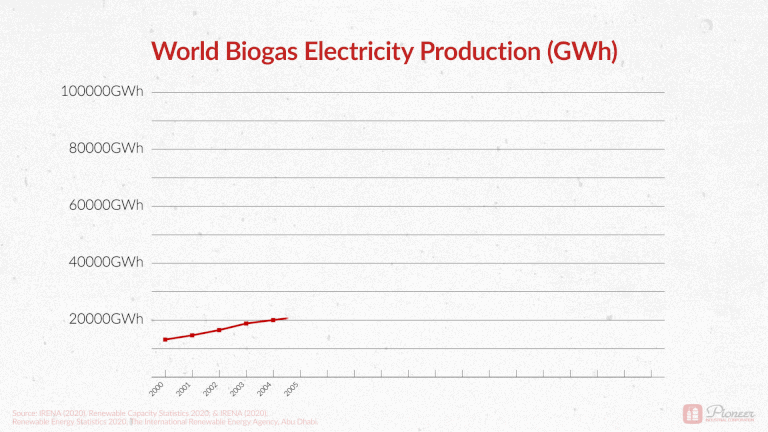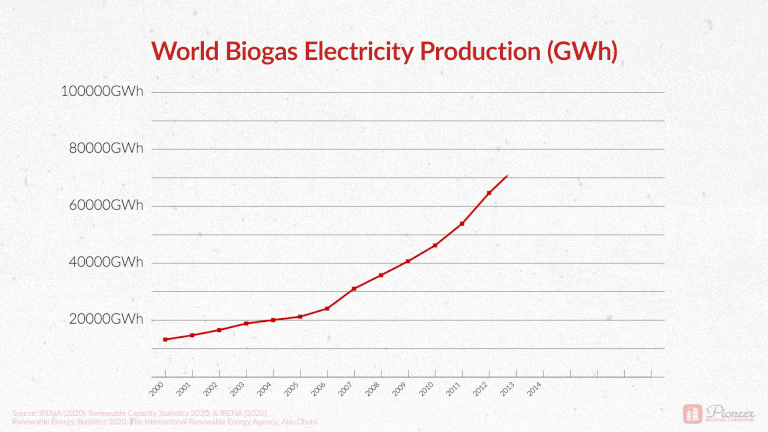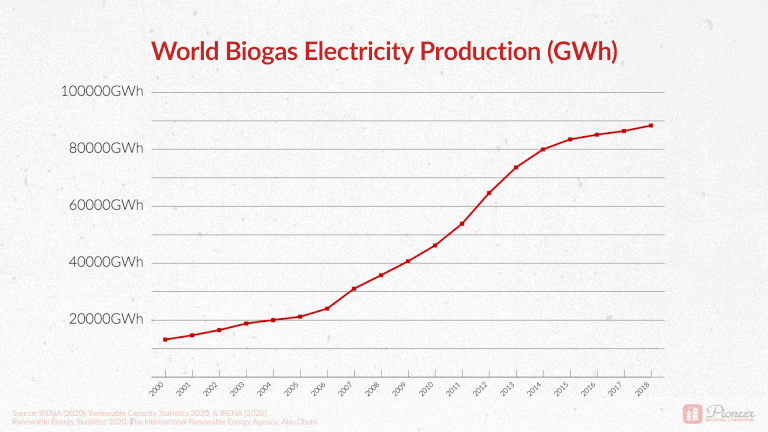
As a point of general interest, we recently shared the following graphic on our LinkedIn page. Global electricity production from biogas has more than quadrupled in the last 20 years! Total production went from 14,000 GWh in 2000 to 90,000 GWh in 2018. A stronger push towards renewable energy has paired with more sophisticated technologies. Turning waste into valuable resources is becoming increasingly attainable.
The Future of Energy
Energy production will always remain a challenge between meeting demands and regulations. Thankfully, we have many different resources and ways of tapping into them. We have hardworking, innovative people and companies continually working on these issues. New, better, and efficient energy production will continue to power our communities.
 Copyright Independent Balkan News Agency, 2021
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Biogas-Plant.jpeg
1048
2000
Karrie Williams
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Pioneer-Logo-Color-min.png
Karrie Williams2021-11-17 21:25:392021-11-17 21:25:44Waste Burner Systems
Copyright Independent Balkan News Agency, 2021
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Biogas-Plant.jpeg
1048
2000
Karrie Williams
https://www.pioneerindustrial.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Pioneer-Logo-Color-min.png
Karrie Williams2021-11-17 21:25:392021-11-17 21:25:44Waste Burner Systems
Harnessing Natural Fluid Flows – An Exploration of Alternative Energy Sources Industries
Environmental Safety, Renewable Energy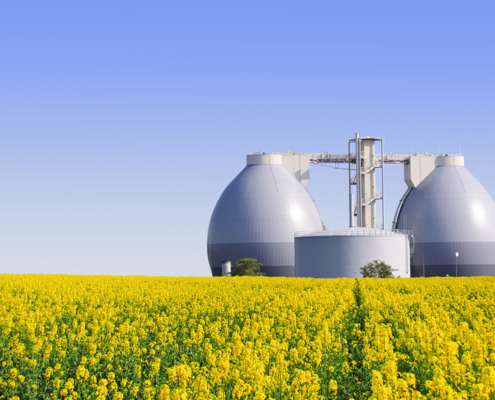 Copyright 2019 © evon GmbH All rights reserved.
Copyright 2019 © evon GmbH All rights reserved.